
Type 1 diabetes necessitates ongoing management and care due to its chronic nature. For individuals with Type 1 diabetes, accessing comprehensive healthcare coverage is essential to ensure the affordability of necessary treatments, medications, and supplies.
Medicare, the government-sponsored health insurance program in the United States, provides coverage and support for individuals with Type 1 diabetes. Listed below are the specific benefits, coverage options, and resources available through Medicare for those managing Type 1 diabetes:
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes
An autoimmune response is the defining characteristic of type 1 diabetes, wherein the body’s immune system erroneously targets and eliminates the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Insulin, a crucial hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels, becomes deficient or absent, leading to elevated glucose levels in the bloodstream, known as hyperglycemia.
Managing Type 1 diabetes involves:
- Carefully monitoring blood sugar levels.
- Administering insulin and following a balanced diet.
- Engaging in physical activity.
- Regularly visiting healthcare providers.
Medicare Coverage for Type 1 Diabetes
Medicare covers individuals with Type 1 diabetes through various parts, each addressing specific healthcare needs. Let’s examine the different Medicare parts and their coverage related to Type 1 diabetes:
1. Medicare Part A (Hospital Insurance)
Medicare Part A covers inpatient hospital care, including diabetes-related hospitalizations. It includes necessary hospital stays, surgeries, and associated medical services. However, it’s important to note that Part A does not cover outpatient or physician services related to managing Type 1 diabetes.
2. Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance)
Medical Insurance covers a range of services related to diabetes management, including doctor visits, outpatient care, laboratory tests, diabetes self-management training, durable medical equipment, and supplies such as glucose monitors and test strips.
Under Part B, Medicare covers 80% of approved services and supplies, while the remaining 20% is typically covered by coinsurance or a supplemental insurance plan. It’s important to review specific coverage guidelines and Medicare-approved suppliers when obtaining DME and supplies.
3. Medicare Part C (Medicare Advantage)
Also known as Medicare Advantage, it offers an alternative way to receive Medicare benefits. Private companies approved by Medicare offer these plans and provide all the coverage included in Parts A, and B. Medicare Advantage plans may offer additional conveniences such as prescription drug coverage, vision and dental care, and disease management programs.
For individuals with Type 1 diabetes, Medicare Advantage plans can provide comprehensive coverage that includes doctor visits, DME, supplies, and prescription medications specific to diabetes management. It’s important to carefully review the details of each plan, including network providers and formularies, to ensure they align with your diabetes care needs.
4. Medicare Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage)
Medicare Part D covers many prescription medications, including those used to manage Type 1 diabetes. It includes insulin, oral diabetes medications, and other diabetes-related drugs. Private insurance companies approved by Medicare offer Prescription Drug Coverage, and coverage options may vary.
When selecting a Part D plan, it’s crucial to consider the formulary, which is the list of covered medications. Ensure that the specific insulin and diabetes medications you require are included in the formulary, and review the associated costs, including deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
Additional Medicare Support for Type 1 Diabetes

Apart from the coverage provided by the various Medicare parts, there are additional resources and support available to individuals with Type 1 diabetes:
Diabetes Self-Management Training (DSMT)
First, Medicare covers DSMT services and education programs designed to help individuals with diabetes effectively manage their condition. DSMT provides essential training on blood sugar monitoring, insulin administration, nutrition, exercise, and overall diabetes self-care. Certified diabetes educators or healthcare professionals typically provide these services.
Participating in DSMT can empower individuals with Type 1 diabetes to take control of their health and make informed decisions regarding their diabetes management. Medicare provides coverage for a maximum of 10 hours of initial DSMT and up to 2 hours of follow-up DSMT per year. It’s essential to consult with healthcare providers or contact Medicare directly to find a certified DSMT program near you.
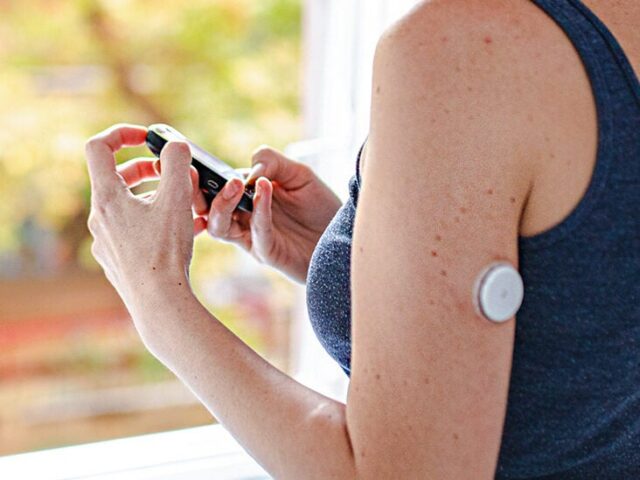
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems
Second, continuous glucose monitoring systems are sophisticated devices that continuously monitor blood sugar levels, encompassing daytime and nighttime periods. These systems provide real-time data, high or low blood sugar level alerts, and trend analysis. For individuals with Type 1 diabetes who necessitate intensive blood sugar monitoring, CGM systems can be immensely beneficial.
Medicare expanded coverage for CGM systems in recent years. Under specific circumstances, Medicare Part B may cover the costs of CGM systems, including the device and necessary supplies. Coverage guidelines apply, and individuals must meet specific criteria to be eligible. It’s essential to consult with healthcare providers and suppliers knowledgeable about Medicare coverage for CGM systems.
Third, Medigap plans are private insurance policies to fill the gaps in coverage left by original Medicare. These plans help cover out-of-pocket costs such as deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments. While Medicare Supplement plans do not cover prescription drugs, they can provide financial assistance for other diabetes-related expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and DME.
It’s important to note that these plans are only available to individuals with original Medicare (Parts A and B) and not those enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans.
Conclusion
Ultimately, understanding the coverage options available through different Medicare parts and additional resources such as DSMT and CGM systems empowers individuals with Type 1 diabetes to make well-informed choices and proficiently handle their condition.
It’s essential to review the specific coverage guidelines, formularies, and enrollment periods associated with Medicare to ensure you maximize the benefits available for your Type 1 diabetes care. Consult healthcare providers, certified diabetes educators, and Medicare representatives to navigate the coverage options and resources that best meet your needs.












