
The Kushan culture was rooted in the traditions of the Yuezhi, a people of Indo-European origin, who established a syncretic empire known for its unique blend of influences. As this empire grew, it transformed the landscape of ancient Asia, both in economic realms and artistic expression.
Its impact can still be felt today, illustrated by the rich archaeological sites that speak to cultural exchange and artistic development. In the pages ahead, we will explore the rise of this powerful empire, the pivotal figures who shaped its destiny, and the enduring influences of Kushan culture that continue to resonate throughout history.
Geographic and Cultural Influence of the Kushan Empire
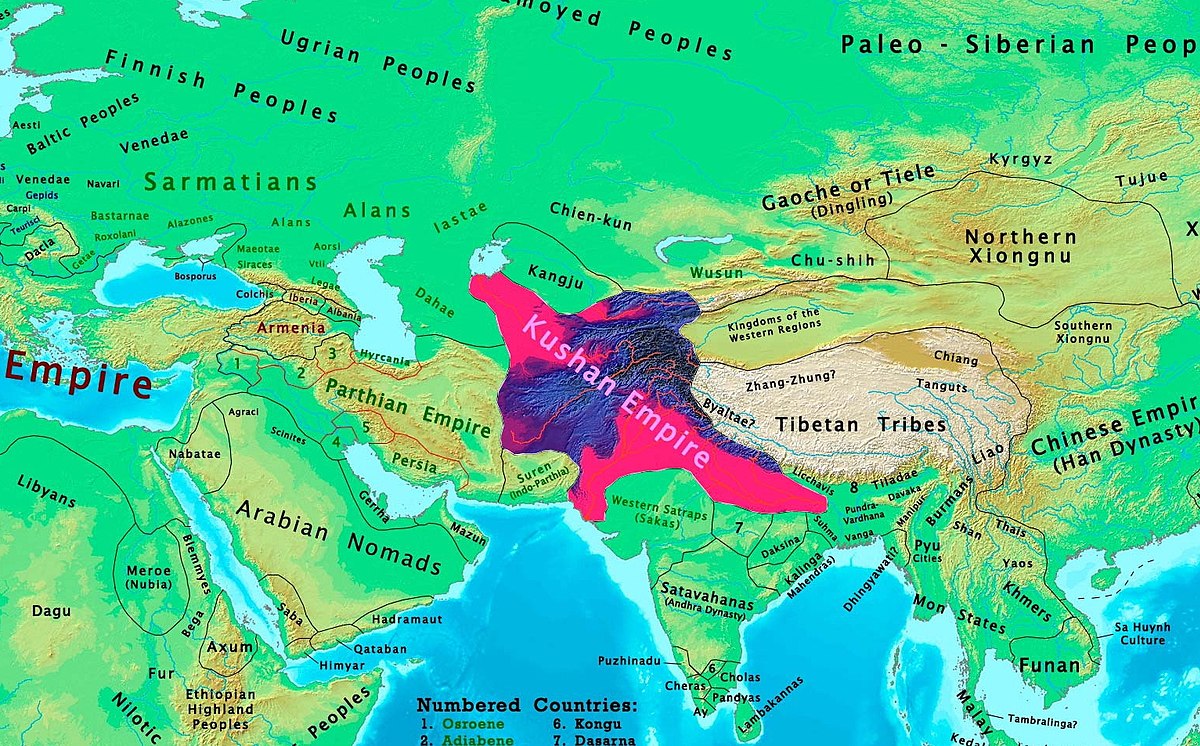
The geographic extent of the Kushan Empire encompassed a vast territory that included parts of modern-day Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and northern India. At its zenith, this empire served as a vital crossroads for trade and cultural exchange. Its location along the Silk Road facilitated interactions between Eastern and Western civilizations, influencing regional dynamics in meaningful ways.
Extent of the Empire
The Kushan Empire’s expansive nature allowed it to control significant trade routes. Through these routes, goods, ideas, and cultures merged, creating a unique environment that fostered economic prosperity. Its capital, Peshawar, emerged as a bustling hub where traders from diverse backgrounds convened, contributing to the growth of the empire.
Cultural Melting Pot of Gandhara
The region of Gandhara exemplified cultural diversity in Gandhara, showcasing a rich tapestry woven from Greek, Indian, and Central Asian traditions. The influence of Hellenistic art is particularly noticeable in the visual arts, where sculptures and architectural forms reflect a blend of distinct motifs. Early representations of the Buddha in human form emerged during this period, illustrating the melding of cultures and artistic styles.
Impact on Languages and Religions
The religious influences of the Kushans had far-reaching implications, particularly in the realm of language and faith. Initially, Greek served as the administrative language within the empire. Over time, this transitioned towards Bactrian and other local dialects.
The Kushan Empire played a crucial role in the propagation of Buddhism, acting as a conduit through which the religion traveled into Central Asia and eventually reached China. This expansion contributed to the evolution of Mahayana Buddhism, illustrating the Kushan Empire’s enduring impact on languages during the Kushan period and spiritual practices in the region.
The Role of Kanishka the Great
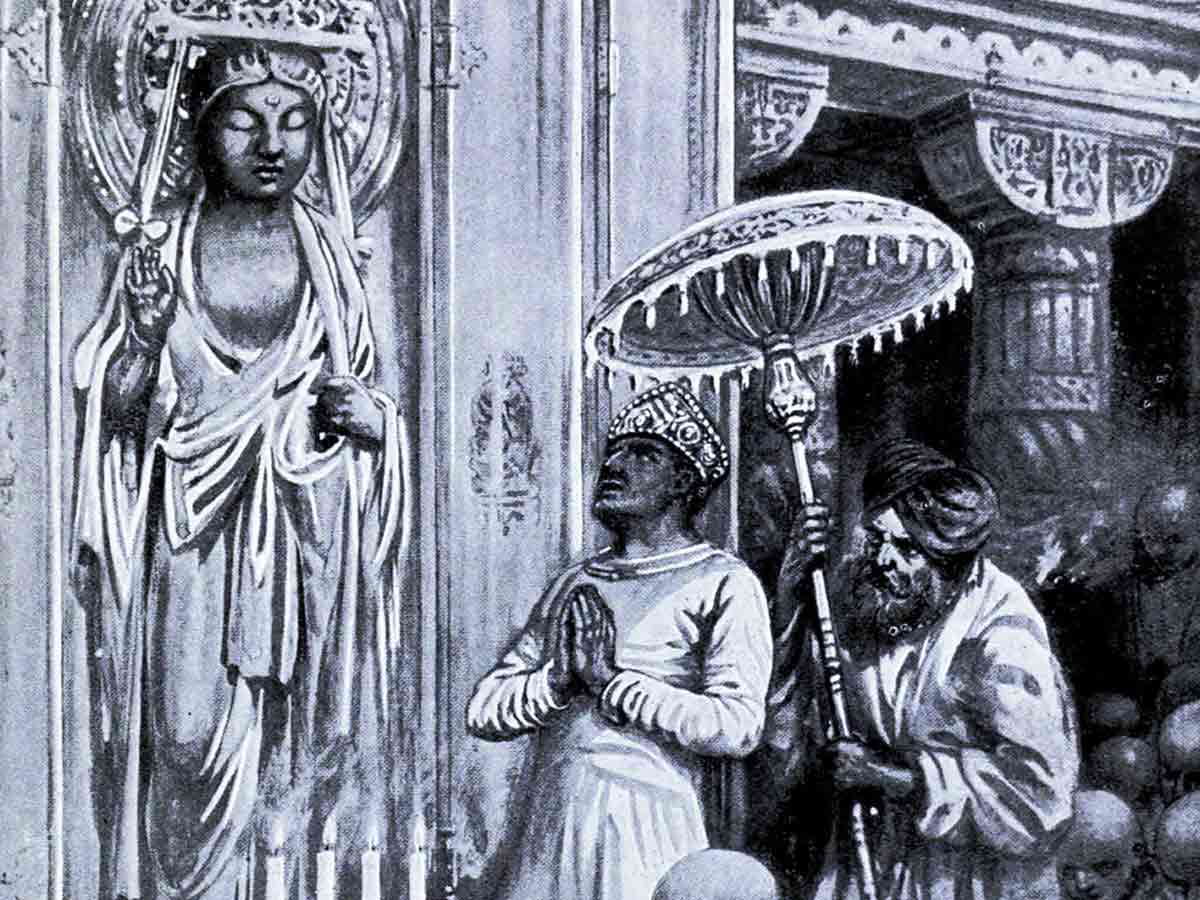

Kanishka the Great played a pivotal role in shaping the Kushan Empire, marking a significant era of expansion and cultural flourishing. His reign extended from around 127 AD, during which the empire not only grew territorially but also became a hub for major cultural and economic developments.
Expansion of the Empire under Kanishka
Under Kanishka, the expansion of the Kushan Empire reached remarkable heights. His leadership allowed the empire to extend into the Ganges Plain and surrounding regions. With his administrative centers established in notable cities like Purushapura, present-day Peshawar, and Mathura, the empire emerged as a formidable power in South Asia.
The military endeavors during Kanishka’s rule facilitated not just the conquest of new territories but also the cultural diffusion that characterized this period.
Promotion of Buddhism and Trade
Kanishka is particularly remembered for his profound support of Buddhism under Kanishka. This support culminated in the sponsorship of the Fourth Buddhist Council in Kashmir, which significantly contributed to the propagation of Mahayana Buddhism.
Alongside this, trade during the Kushan period flourished. Kanishka’s policies established vital trading routes that connected the East and West. This trade network not only stimulated economic growth but also fostered rich cultural exchanges, enhancing the cultural fabric of the empire.
Relations with Other Civilizations
Kanishka’s administration actively pursued diplomatic relations with other great powers of the time, founding connections with the Roman Empire and Han China. These relationships solidified Kushan dominance along the Silk Routes, transforming the Kushan Empire into a cultural and economic bridge between Eastern and Western civilizations.
Such interactions laid the groundwork for a period of profound intellectual and commercial exchange, reinforcing the significance of the Kushan Empire in ancient global history.
The Artistic Legacies of the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire contributed significantly to the cultural landscape of ancient Asia, particularly through its art forms. Characterized by a unique blend of indigenous and foreign techniques, Kushan art remains a vivid representation of the artistic influence of the Kushans during their reign.
This section explores the defining features of Kushan art, its contributions to the Gandhara civilization, and the integration of Greek and Buddhist art that marked this transformative period.
Kushan Art and Its Characteristics
Kushan art is distinguished by its sophisticated style and attention to detail. Artists skillfully amalgamated various influences, especially those from Hellenistic traditions. The resulting works include intricate sculptures, ornate coin designs, and grand architectural structures. Notable characteristics involve:
- Realistic human forms and expressive facial features
- Use of intricate patterns and motifs
- Combination of religious and secular themes in artwork
Contributions to the Gandhara Civilization
The Kushan Empire played a vital role in shaping Gandhara civilization art, which flourished during its rule. The profound cultural impact led to the construction of remarkable structures such as stupas and temples. Various art forms emerged, including:
- Elaborate stone carvings depicting various deities and narratives
- Mazestic Buddhist monasteries that served as centers for spiritual learning
- A distinctive artistic idiom influenced by local and foreign styles
Influences of Greek and Buddhist Imagery
The artistic influence of the Kushans is particularly evident in the seamless integration of Greek and Buddhist art. This fusion resulted in unique representations of religious themes and iconography. Key aspects of this integration include:
- Adoption of classical Greek artistic techniques, such as drapery and spatial perspective
- Representation of Buddhist deities with Hellenistic features, enriching the visual narrative
- Creation of syncretic art that resonated with diverse audiences
Conclusion
The summary of the Kushan Empire reveals a civilization that played a crucial role in the development of ancient Asia. Its unique ability to blend various cultures and religions facilitated significant advancements, particularly in the realm of Buddhism. As it emerged as a melting pot, the empire created an environment where trade and artistic expression flourished.












